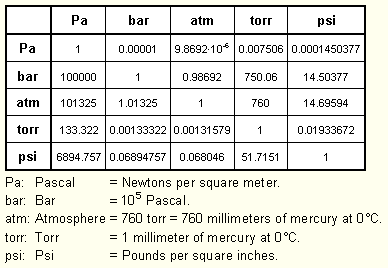
The rules for Quantum Numbers are as followed:
1. Principle Quantum Number: (n) this is the principle energy level
2. Angular Momentum Quantum Number: (l) this number determines the type of sublevel. The numbers are 0,1,2,3 for s,p,d,f
3. The Magnetic Quantum Number: (m1) this number runs from -1 to +1: whatever orbital you are in
4. The Spin Quantum Number: (ms) This is +1/2 for the first electron in an orbital and -1/2 for the second electron in an orbital
This concept may seem difficult but after going over it multiple times it got easier here are some examples below:
Determine the electron for the following set of quantum numbers.
- 3,2,0,-1/2: 3d^8
- 2,1,1,1/2: 2p^3
Or assign the quantum numbers for each electron below:
- 1s^1: (1,0,0,+1/2)
-1s^3: Does not exist